
How are youth rights discussed in Turkey? Can we mention a youth policy?
Unfortunately, youth rights are not legally defined in Turkey. Besides they are undefined, there is no youth policy that comprehends youth rights either. Hence there are significant problems of achieving the rights, considering they are neither defined nor written. Young people are stuck with the definition of “ decent youth.”
They are facing with pressure and discrimination when they step outside of this definition. Hence some of the research that had been done lately show us the results of this situation. The young people, who are infelicitous and have a tendency to leave the country as a future plan, are at the top of the research.
There is a generation Z which have been on the radar of most people lately. They become the subjects of arguments and political parties. However, young people have no active participation in decision-making mechanisms. You have been studying this very topic for a long time. What would you like to say?
Youth have been remaining on the agenda in two headlines. The first one is their significance in the context of capital, the other one is their significance in elections.
The reason for generation Z remains on the agenda is that they create a major part of voting in an election. I anticipate we went through this argument because competent had realized the alteration of generation and created a youth policy that contains the altered needs of young people.
Young people, who belongs to generation z, have been demonstrating the activism that is a pioneer of an environmental act which has the strength to shake governmental policies. Well, what are we discussing, then? The voting behaviors of generation z.
The youth have always been the subject of the arguments about their greatness on population and, due to this fact, about their labor force and power of voting. Because of the sense and the policy about young people is this, they are not able to be a participant in decision-making mechanisms. The fight of the youth in Turkey is the fight of being an individual of the youth - this fact occurs both in decision-making mechanisms and social life. The major operator of decision-making mechanisms is political parties. However, young individuals are not able to participate in administration systems of political parties. They are stuck in the structure of “youth branches.” Hence, when there is an election the “youth branches” play a major role in the labor force by putting up a poster, organizing the street and in all of the field labor.
I would like to ask about the timeline that we are going through. During the COVID-19 pandemic, which violations of rights had occurred towards young people?
In the pandemic, the citizens that are under 20 faced social pressure due to curfew. Because of online education, young people who cannot access computers or the internet had experienced inequality of opportunity. Some young individuals were forced to live their KYK dorms hence their housing rights had been violated. Daily jobbers could not be reached their right to labor. The young people who had been deprived of their freedom due to thought crime had nor been released from jails in the era of amnesty. Some suppliers of scholarship had cut off their grants due to online education. The ones who are economically disadvantaged had to vacate their houses and had indwelled in temporary shelters due to travel restrictions. These are some of the violations of rights and some prior problems that happened.
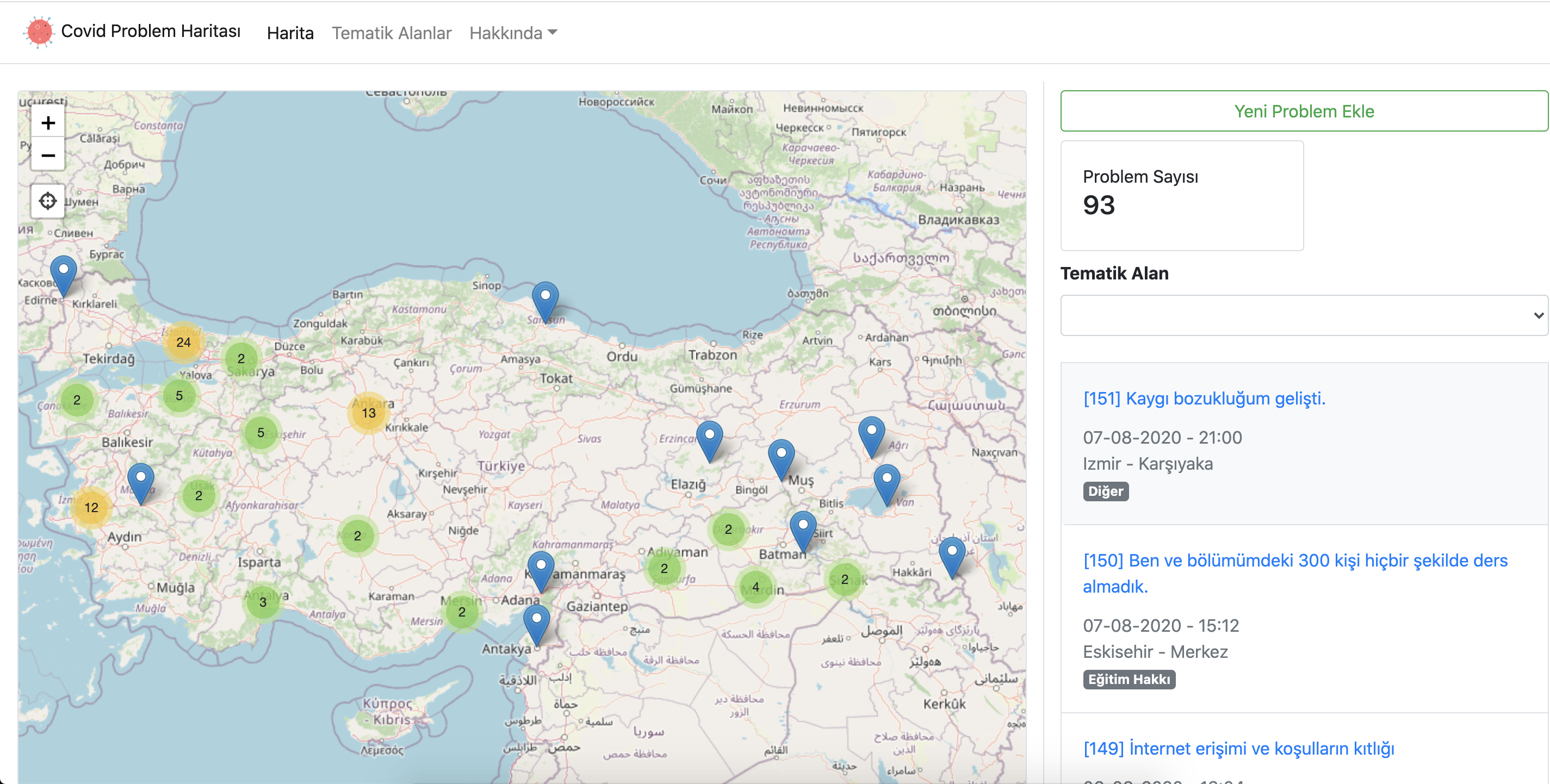
We started a mapping study to be able to track young people’s problems of reaching their rights in the pandemic. 54 violations of right had been reported since we began mapping. The most prior violations are in the field of education and labor. Housing and health follow after these two fields. The problems of education originated from not being able to access computers or the internet and the incorrect application of online education by schools. In the field of labor, the ones who are fired, cannot receive their money or forced to take a break are creating the majority.
Due to intensity of population, Istanbul and Ankara are on the top of reported violation of rights. In the context of the region, we did not receive any violations from the Blacksea region yet.
On the other hand, It is a reality that the young individuals who entered data to GoFor map of violations of rights are the ones who have access to computers and the internet. 42% of the data had been entered anonymously. This data shows us that young individuals have the fear of being labeled because of sharing their problems in public.
In the pandemic, the ones who experienced curfew was the youth. However, in the application, they did nor treated “equally.” What are the reflections of this?
Turkish Statistical Institute announced that there are 12 million 955 thousand people young people between the age of 15-24. One of the most significant mistakes is assuming these 13 million people have the same needs during the process of putting the policies about young people into practice. In the era of the pandemic, the same perspective can be observed in the context of measurements. For instance, the prohibition of labor towards young people did not occur beforehand furthermore they continued working even though they are in the group of risk.
The observations during the pandemic say to us that, in the eye of competent young individuals’ reflection on the capital is more valuable than young individuals. In addition to this, domestic violence towards young individuals increased due to the obligation of staying at home without considering the young individuals’ needs. Of course, these are the observations for the individuals who can reach their housing rights.

